
 Xin Liu, Ph.D candidate
Xin Liu, Ph.D candidate
161 Louis Pasteur, CBY A030
Ottawa, Ontario, Canada,
K1N 6N5
Tel: (613) 562-5800-ext 6875
Email: liuxin429go@gmail.com
Department: Environmental Engineering, University of Ottawa
Research
Interests:
Computational Hydrodynamics
Numerical modeling of Shallow water system
Hyperbolic system governing sediment transport and bed evolution
Gas-particle two phase flow in equipment
Renewable energy: Biomass gasification; Solar energy transportation,
Heat exchange piles
Selected
Publications:
1. X. Liu, A. Mohammadian, A. Kurganov, J.A. Infante Sedano.
Well-balanced fully coupled central-upwind scheme for shallow water flows over
erodible bed. (Submitted in 2014)
2. X. Liu, A. Mohammadian, J.A. Infante Sedano. A robust well-balanced
and fully coupled 2-D model for dam break flow over erodible bed. (Submitted in 2014)
3. X. Liu, A. Mohammadian, J.A. Infante Sedano. A well-balanced 2-D
model for dam break flow with wetting and drying. (Submitted in 2013)
4. X. Liu, J.A. Infante Sedano, A. Mohammadian. One dimensional
numerical simulation of bed changes in irrigation channel using finite volume
method. Irrigat Drainage Sys Eng. (2012)
5. X. Liu, W. Chen, et al. 3D numerical simulation of flow structure in
miniature biomass circulating fluidized bed gasifier. Transact of the Chin
Society for Agricultural Machinery. (2011)
6. X. Liu, W. Chen, et al. Various Circulating Fluidized Beds biomass
gasifiers. Boiler Technology.
(2011)
7. W. Chen, X. Liu. Three-Dimensional Simulation of Gas-Solid Flow in
the Biomass Circulating Fluidized Bed Gasifier��s Riser. Advanced Materials
Research. (2010)
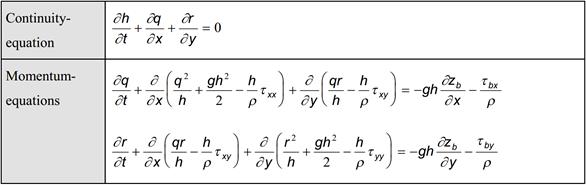
Numerical modeling of shallow water system
The shallow water equations are a set of
hyperbolic partial differential equations derived from depth-integrating the
Navier-Stokes equations, in the case where the horizontal length scale is much
greater than the vertical length scale. Shallow water equations have been
widely used in various engineering fields, e.g. river flow modeling, dam-break
and flood prediction, coastal engineering, harbor engineering, tidal waves
simulation, tsunami prediction, simulation of atmospheric circulation, etc.

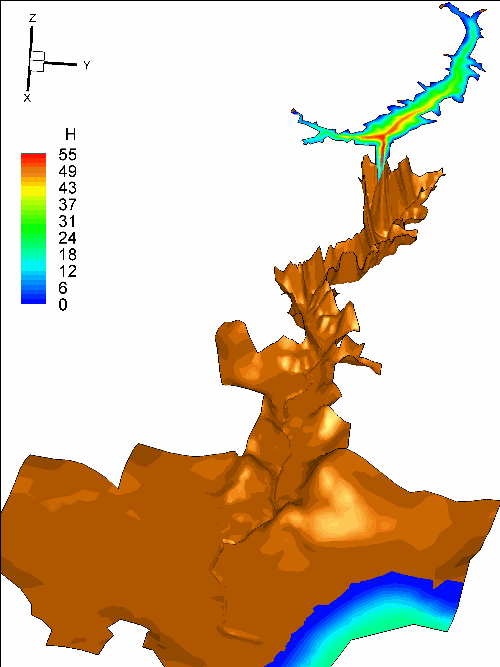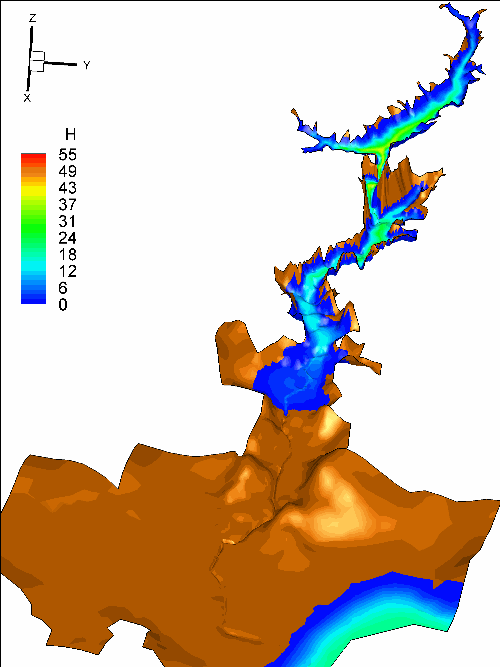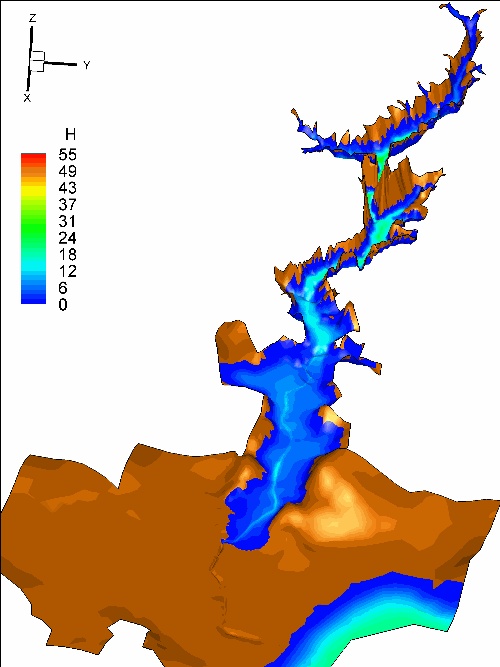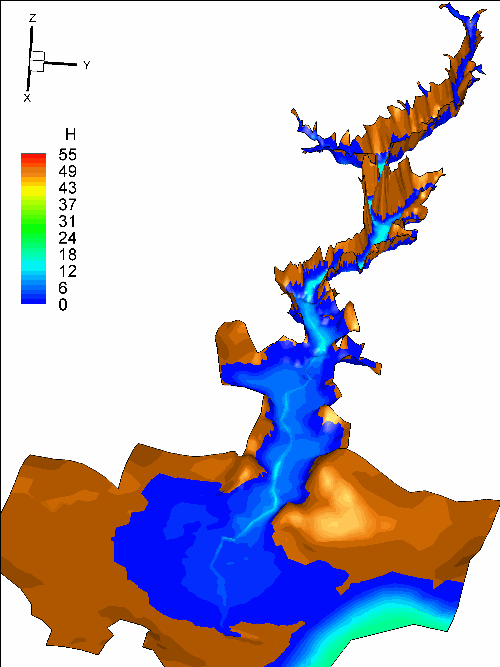
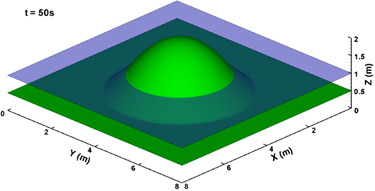
In my research, the shallow water system is applied to
simulate the dam-break flow, wave propagation and flood process based on Finite
volume method. In the model, the second order accuracy both in time and space
is achieved, the well-balanced property is preserved and technique for tracking
wetting and drying fronts is adopted. For high-energetic flow like dam-break
process, non-negative water depth reconstruction and implicit splitting
treatment for friction term are applied to maintain the stability. Thus a
robust 2-D model for shallow water system which can deal various flows over
irregular topography is built.


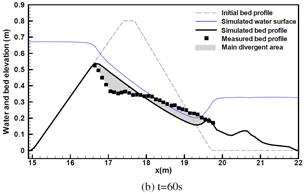
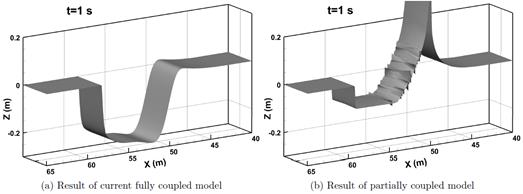
Sediment transport and Bed erosion
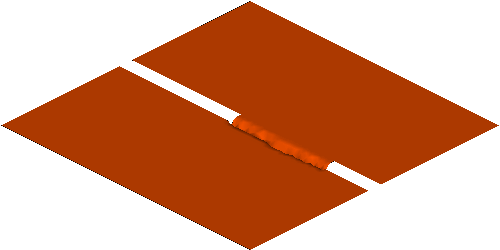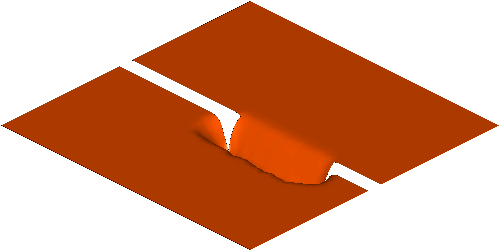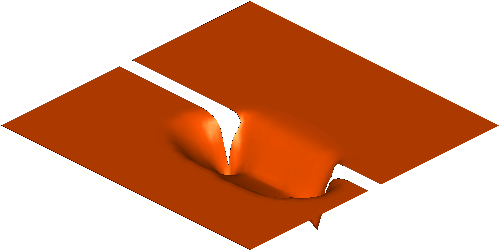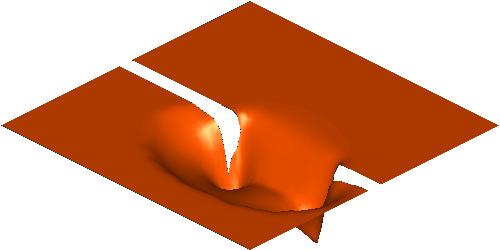
Rapid morphological evolution and intense sediment
exchange with relative high sediment concentration frequently occurred in
high-energetic flows over erodible bed. In my research, the conventional
shallow water equations for clear water needs additional terms considering the
interaction, momentum exchange and overall mass conservation between water and
sediment and thus represents the system of water-sediment mixture. Moreover, to
simulate the strongly coupled simultaneous physical processes consists of water
flow, sediment transport and bed erosion, a fully coupled strategy is applied
by building a truly hyperbolic system.



Gas-particle two-phases flow in equipment
Gas-solids fluidization is widely applied in industry,
including petroleum, chemical, metallurgical and energy industries. In my past
work, the fluidized bed is used for biomass gasification to produce combustible
gas. Using the Gidaspow model for calculating the momentum exchange
coefficient, and taking mutual influence of different mechanic parts in
consideration, simulation of a full-loop miniature circulating fluidized bed
gasifier (CFBG) is taken and it focuses on the gas-solid flow structure in the
riser. The heterogeneous behavior in the CFBG riser and the radial profiles of
solid volume fraction under different solid inventories are investigated as a
replenishment of certain data those are difficult to measure in experiments.
The results showed it can��t form an obvious core-annulus flow because of the
riser��s high height-diameter ratio and the big re-feed pipe diameter. There are
clusters growing and dissipation in a short time. A turning point of pressure
drop may be seemed as a separation of dense area and dilute area. The
three-dimensional (3D) simulation revealed the solid flux and the pressure drop
agree with the experimental data.
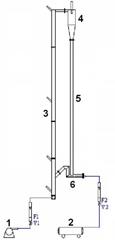
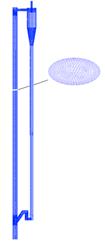
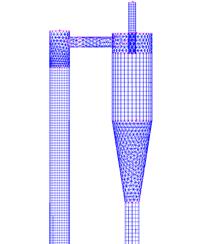
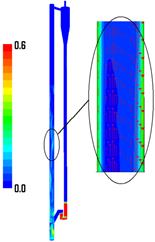
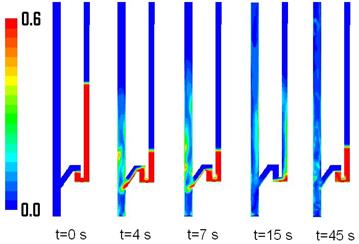

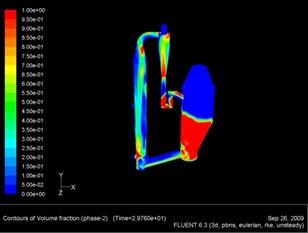
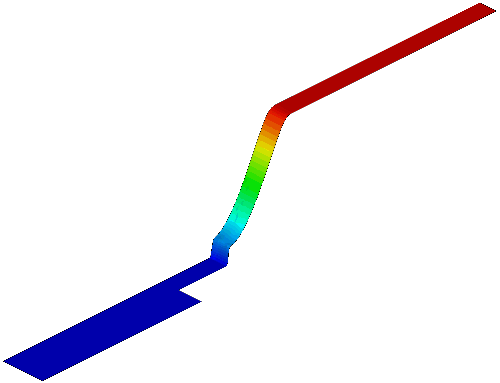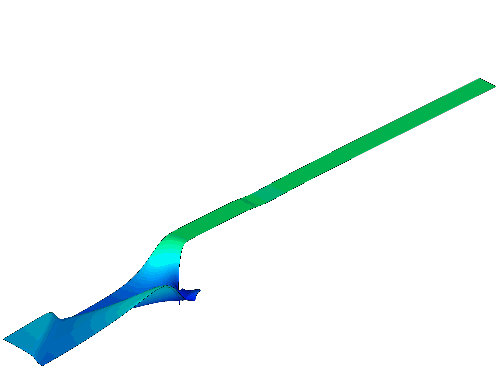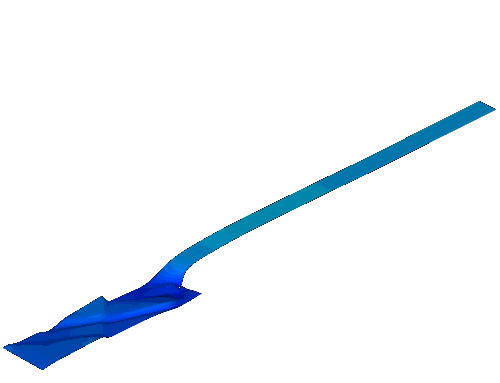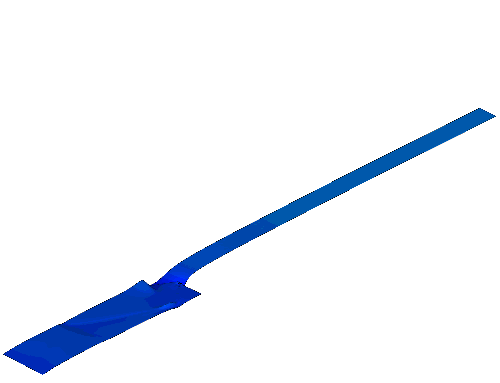
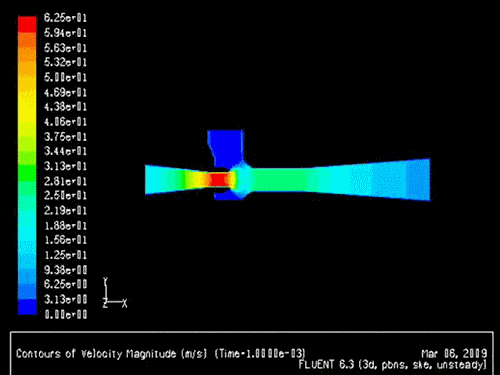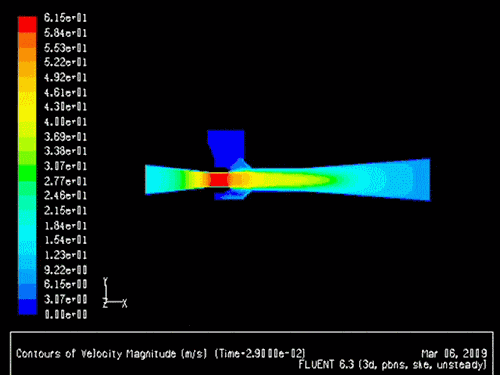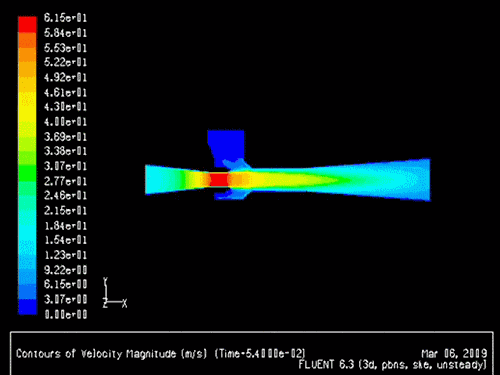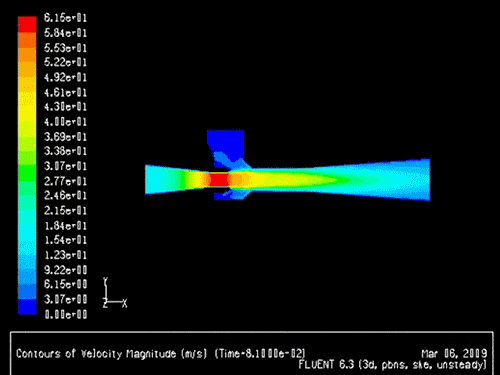
The gas-solid injector could be used to add raw material to
reactor. A 3-D simulation case of
gas-solid injector conducted in 2009 by Xin Liu is presented.


Renewable energy projects
Biomass gasification means incomplete combustion of
biomass resulting in production of combustible gases consisting of Carbon
monoxide (CO), Hydrogen (H2) and traces of Methane (CH4).
This mixture is called producer gas. Producer gas can be used to run internal
combustion engines (both compression and spark ignition), can be used as
substitute for furnace oil in direct heat applications and can be used to
produce, in an economically viable way, methanol �C an extremely attractive chemical
which is useful both as fuel for heat engines as well as chemical feedstock for
industries5. Since any biomass material can undergo gasification, this process
is much more attractive than ethanol production or biogas where only selected
biomass materials can produce the fuel. Circulating fluidized bed gasifier is a
kind of advanced gasification plant which has high heating rate, high reaction
speed and high gas calorific value. It could apply to gasification generating,
liquefaction and so on well. It has a high intensity of gasification and no
moving components in it. So the gasification facility is suited to be
large-scaled and industrialized.




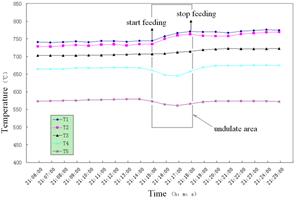


Storage of solar energy for the use at night is a challenging issue. One
of the methods used in practice is to use latent heat and store energy in
reservoirs of molten salt. The objective is this project is optimal design
of phase-change heat storage systems and estimation and minimization of
heat loss in such systems. The heating loss of transporting pipe and reservoir
are predicted for facility optimizing and design.

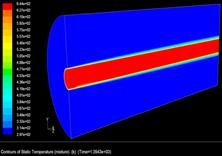
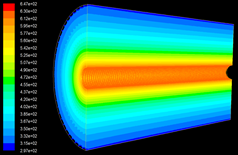
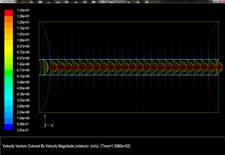
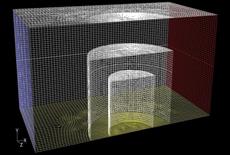
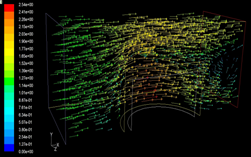
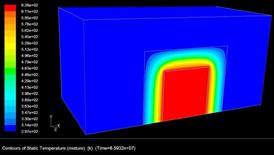
Ground heating requires exchange piles are buried in
the underground. However, the moisture transfer in unsaturated soil will affect
the heating efficiency and waste extra energy. Using dry hot wind to remove the
moisture around piles in soil is one of the feasible methods. An experimental
study and numerical prediction of moisture removing is conducted.


